The Siege of Naxos, which took place in 499 BC, was the first act of the Persian Empire against the Greek city-states and a clear message of what was to follow. Essentially it was the attempt made by the tyrant Aristagoras of Miletus, under the support of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great (father of Xerxes), to conquer the island of Naxos and the neighboring islands. It is widely recognized as the opening act of the Greek-Persian Wars, which would ultimately last for 50 years culminating in the final defeat of the Persians on mainland Greece 11 years later by the united Greeks at Plataea.
The historical accounts are as follows: Iona was the name of a small area of land on the western coast of Asia Minor. Many of the islands between Ionia and mainland Greece were independent. Among these were today’s Sporades to the north and the Cyclades neighboring the mainland. These latter islands were important trade routes the largest and richest among them was Naxos Island.
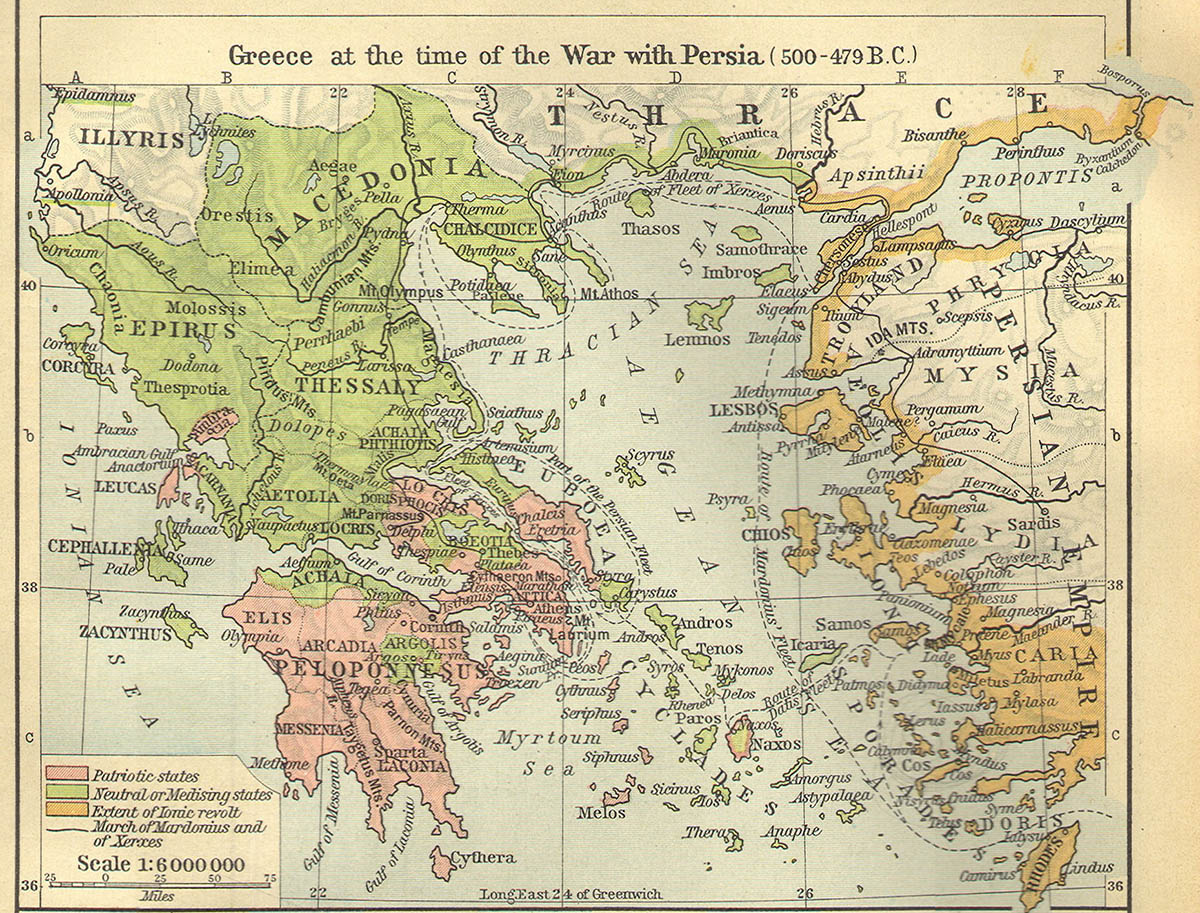
Around the year 546 B.C., Cyrus of Persia (former ruler pre Darius the usurper) crowned himself King of Kings and in the process annexed the Cyclades. He immediately instated higher taxes and placed tyrant rulers creating much dissatisfaction and unrest among the people of the new lands. The result of this action was the Revolt of Naxos. The angry people of Naxos successfully drove away a number of nobles from the island in protest to the measures they supported. The banished aristocrats sought to regain control of Naxos with the help of the tyrant ruler of Ionia's largest city, Aristagoras of Miletus. Aristagoras sensed he would be able to annex Naxos for himself once the conflict ended. The task of doing so required more resources that he could muster compelling him to approach the Persian satrap (local lord) Artaphernes asking him for help.
Artaphernes appointed Megabates Darius’ cousin to see the task through. On the journey to Naxos, Aristagoras and Megabates quarreled and the historian Herodotus suggests that Megabates informed the Naxians of the imminent arrival of the force. The expedition ended in a debacle. When they arrived, the Persians and allied Ionians were faced with a city well prepared to undergo siege. The expeditionary force dug in to besiege the defenders and ran out of money four months later forcing their return to Asia Minor without success. There is some speculation as to whether it was Megabates who warned the Naxians or Aristagoras, since a failed expedition would have cost massive amounts of money and political fallout in Persia whith ensuing consequences. Some suggest that it was Aristagoras instead who informed the Naxians to avenge the previous fallout he had had with Megabates.
In the aftermath of the disastrous expedition, sensing danger and fearing consequences from an enraged Darius, Aristagoras incited the whole of Ionia into rebellion against Darius. The revolt eventually spread to Caria and Cyprus both of whom were under Persian control. A Persian campaign across Asia Minor followed for three years with no decisive effect in their attempt to quell the rebellion. Eventually, the Persians regrouped and crushed epicenter of the rebellion at Aristagoras’ hometown of Miletus. Aristagoras had enlisted the help of the Eretrians and Athenians in his attempt to ward off the Persians. This placed them squarely against the Persians who would not forget their role and would consequently put them in his sights.
The ensuing Battle of Lade, proved to be the harbinger of Aristagoras’ final undoing, he was murdered several years later in Thrace. The Persians decisively defeated the Ionian fleet and effectively crushed the rebellion. Asia Minor had been brought back into the fold and Darius vowed to punish the Athenians and Eretrians, who had supported the revolt causing him so much trouble. The first Persian invasion of mainland Greece In 492 BC would begin as a consequence of the failed attack on Naxos. That too failed…
Take a quick tour on Naxos island and discover its most impressive features. You may start with the following:
What's new (or old) on Naxos, from our blog articles.